Today in modern dermatocosmetology warehouses there are many methods to correct various aesthetic skin imperfections - chemical exfoliation, mechanical dermabrasion, laser coating, microdermabrasion, contour plastics. However, new directions and technologies in the beauty industry are constantly evolving and improving. p>
This trend is special for hardware methods, especially for laser medicine. The use of lasers, first in dermatology, and later in cosmetology, has had an impressive period. Even since the emergence of one of the newest methods of laser treatment - selective phototrolysis - it has been more than 25 years. The pioneers in this direction, American RR Anderson and JA Parrish, have determined the fate of fractional lasers in medicine, making them indispensable in the aesthetic treatment of skin imperfections such as capillary hemangiomas. Port grape stains, hypertrichosis, tattoos, rosacea, pigmentation disorders, photosynthesis, wrinkles, etc.
Modern skin remodeling techniques
We live in a time when more people live to old age than before. And since many of them continue to live active lives, one of the most important problems in aesthetic medicine is to fight skin aging.
Plastic surgery is able to rejuvenate the shape of the face by removing excess skin. However, at the same time, the skin still changes with time (age-related aging) or external factors (pictures). It is also important that most patients want to look younger without surgery.
In this case, what methods should be used to affect the skin and what should happen in it for true rejuvenation?All methods that can be used to improve the appearance of the skin are combined by one principle - they apply a traumatic effect on the skin, provoking fibrosis, which in turn causes tension and compaction.
Currently, dermatocosmetology uses three main types of remodeling effects on the skin, including:
- chemical stimuli - chemical exfoliation with acids (trichloroacetic, glycolic, etc. );
- mechanical stimuli - mechanical dermabrasion, microdermabrasion, mesotherapy, fillers, needle division;
- thermal stimulation - laser ablation, thermolifting using laser and broadband light source, radio frequency lifting, fractional method.
Chemical stimuli
Historically, acid exfoliation (exfoliation) was the first method of skin rejuvenation. The principle of exfoliation is partial (such as superficial exfoliation) or almost complete (such as middle and deep exfoliation) destruction of the epidermis, damaging the structure of fibroblasts and dermis. This damage activates the inflammatory reaction (the stronger, the greater the amount of self-destruction), which leads to the production of extra collagen in the skin.
However, to achieve the desired results, exfoliation must be at the expense of the epidermis. Experiments with burns have misled many people, who allegedly "proved" that the epidermis is a self-renewing organ that quickly recovers from damaged areas. In this case, exfoliation so that for some time becomes more aggressive on the epidermis (e. g. , deep phenolic exfoliation), until finally the accumulated problems make experts realize this evil method that eventually leads to thinning of the skin.
Deep exfoliation supporters ignore problems that arise. Their essence is that due to the destruction of the dermis papillis and poor nutrition, the epidermis becomes thinner, and the number of cells in the thorny layer decreases significantly compared to what was previously peeled. Decreased barrier function of the stratum corneum causes a decrease in skin hydration. (Thus, almost all patients after prolonged exfoliation experience severe dryness of the skin) At the same time, the introduction in lighter skin practices (using trichloroacetic acid and fruit) did not meet their expectations to tighten the skin effectively.
Mechanical stimulation
From the method of mechanical stimulation of crop changes on the skin, dermabrasion with the use of a rotary tool (with a velocity v; rotary cutter up to 100, 000 rpm) needs special attention. Currently, modern Schumann-Schreus devices are used (German)
This method can only be used in surgical hospitals, as this procedure requires anesthesia, postoperative treatment of the wound surface, a special toilet for the eyes and mouth, as well as a device for feeding the patient (due to the fact that significant postoperative edema occurs 2-3days after the procedure complicate the opening of the eyes and mouth).
This method is very effective, but, unfortunately, with mechanical dermabrasion there is a high risk of complications such as:
- postoperative hyperemia;
- the appearance of the depigmentation area due to the destruction of melanocytes when the cutter penetrates the basement membrane;
- wound surface infection;
- scars (if the cutter is too deep to sink into the skin)
All of the above have determined the limited use of this method in clinical practice.
Thermal stimulation
Ablative remodeling
Since the late 1980s, lasers have been used to rejuvenate the skin with tissue removal by layer (ablation) [4]. Removal of the surface layer of the skin with low trauma using a carbon dioxide laser stimulates its own collagen synthesis in it, the amount of which increases several times after the procedure. Then gradually rearrange.
The most effective is the use of CO2 lasers, when exposed to deep thermal effects on all layers of the dermis, which are externally indicated by the skin tightening effect. This method is called "laser dermabrasion", or "laser re-emergence", and in terms of efficiency can not be compared with other skin rejuvenation methods available at that time (Fig. 1).
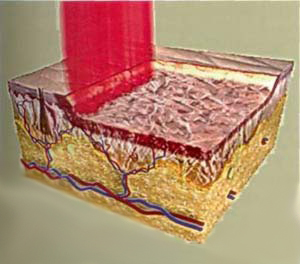
Figure. 1. Natural laser surface laser scheme (dermabrasion laser)
However, CO2 lasers also cause a large number of complications. In addition, further studies show that the profound effect on the dermis stimulates the formation of fibrous tissue to a greater extent than that which contributes to the new synthesis of normal collagen-oriented [5]. Growing fibrosis can make the skin look pale naturally. Collagen synthesized after treatment is reabsorbed after a few years, like collagen formed at the scar site. As a result of thinning of the epidermis caused by atrophy of the papillary layer of the dermis, fine wrinkles begin to appear on the skin. Due to the weak barrier function of the stratum corneum, the level of skin hydration decreases, and it looks atrophic.
Laser garnet-erbium Erbium-aluminum-yttrium appears later. Advantages of erbium lasers such as superficial heat penetration depths (erbium lasers penetrate to a depth of 30 μm, CO2 lasers - up to 150 μm) and (consequently) lower risk of burns and tissue carbonation, as well as relatively low prices (compared to carbon dioxide lasers), attracting the attention of many experts around the world.
However, as experience of working with these two types of assemblies accumulates, opinions have grown among experts that CO2 lasers are more efficient [6]. Although there is a negative effect of carbon dioxide laser dermabration described above, the initetap method is needed for acne scar correction. In addition, it can be considered an alternative to surgical skin tightening - of all remodeling methods, only exposure to CO2 lasers can actually cause collagen shrinkage with a visible clinical lifting effect.
The problem with all the methods described above is that they often "sacrifice", that is, significantly damage the epidermis. To rejuvenate your skin and really look young, you need a perfect epidermis with natural dermis papillae, good hydration, normal skin color and elasticity. The epidermis is a very complex highly specialized organ, up to 200 microns thick, which is our only defense against the effects of negative environmental factors. Therefore, whatever we do to rejuvenate the skin, we need to make sure that the underlying architecture is never damaged.
This concept contributes to the emergence of non-ablative skin remodeling technology.
Non-ablative remodeling
The most common devices for non-ablative skin remodeling are neodymium (Nd-YAG) and diode lasers, as well as broadband light sources (IPL). The principle of their action - selective phototrolysis - consists of heating and destruction of structures, containing sufficient amounts of melanin or oxyhemoglobin. In the skin, each is a collection of melanocytes (lentigo, melasma) and micro-vessels (telangiectasia). The wavelength emitted used in non-ablative lasers corresponds to the maximum absorption spectrum of oxyhemoglobin or melanin. Non-ablative and IPL laser treatment procedures are relatively safe, the recovery period is minimal, but such treatment only removes pigmentation and vascular cosmetic defects. In this case, there is a certain thickening of the skin, but the effect obtained is not long.Fractional Skin Recovery Techniques
The constant search for effective and rejuvenating skin rejuvenation methods has led to the emergence of revolutionary technology - the delivery of laser radiation fractions. The proposed skin rejuvenation method has been specially designed to overcome some of the above difficulties. Unlike conventional "ablative and non-ablative laser methods, which are designed to achieve uniform thermal damage to the skin at a certain depth, the fracture method makes it possible to achieve selective microscopic thermal damage in the form of many modified poles and leaving unaffected areas around the micro lesions. this. Currently, the industry produces two types of fractional lasers: non-ablative and ablative.
The first uses erbium-doped optical fiber that produces radiation at a wavelength of 1550 nm. Fractional lasers form on the skin of thousands and tens of thousands of micro damage in the form of columns - microthermal treatment zone (MLZ) - with a diameter of 70-150m depth to 1359 mcm As a result, about 15-35 skins are photocopied in the treated area. Chromosomes for lasers are water. Freezing occurs mainly in the lower layers of the epidermis and dermis. The stratum corneum remains intact as it contains relatively little water, and this reduces the risk of infection. Rapid epidermal recovery is due to the low number of lesions and the short migration distance of keratinocytes. The healing period is accompanied by moderate olehedema and hyperemia, followed by desquamation, appearing on days 5-7. Patients practically do not lose social activity. This technology - frotional photothermolysis (FF) - is a very effective non-ablative fractional skin remodeling method. To achieve the desired effect, course treatment is prescribed. Depending on the clinical condition, it is recommended to perform from 3 to 6 procedures with an interval of 4-6 weeks. Like other non-ablative skin remodeling methods, the end result can be seen only 4-8 months after the procedure (cumulative effect).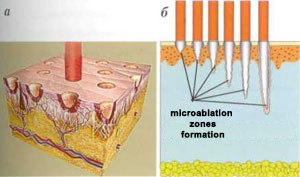
In cases where a more aggressive effect on the skin is needed - for scar correction, removal of deep wrinkles and excess skin, the fractional ablation method (FA, or dermal ablation in fractions -FDDA) is used.
Fractional ablation methods combine the advantages of CO2 lasers and fractional principles of laser radiation delivery. In contrast to traditional CO2 lasers, which remove the entire layer of skin surface by layer, the FA unit forms a large number of microablatifzon (MAL) with a diameter of up to 300 µm at a vapor depth of 350 to 1800 µm (Fig. 2).
Therefore, during this procedure, laser radiation penetrates the deep layers of the skin, damaging the top layer of the epidermis. In terms of efficiency, ablative fractional laser rejuvenation can be compared to plastic surgery, this is how much in the laser beam reappears.Figure. 2. Principles of ablative fractional laser operation: formation of microablative zones - MAZ (a); dependence of MAZ formation depth on laser radiation power (b)
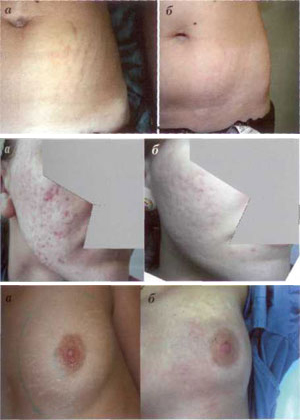
As in FF, from 15 to 35% of the skin of the treated area is actually exposed (in some cases, up to 70%). Recovery after FA procedure is faster than after layer-by-layer coating. This is due to the fact that the epidermis and stratum corneum remain intact. Skin bleeding was observed for some time immediately after the procedure, but immediately stopped (Fig. 3 a, b).
Figure. 3. Step-by-step skin recovery after fractional ablation procedure: see as soon as treatment (a); every other day (b); after 5 days (c); 14 days (d) after one procedure
A number of bloody microbes appear in the dermis, causing the flow of complex changes that lead to the production of new collagen. Once the bleeding has stopped, it is necessary to remove the remaining serous fluid on the surface of the skin. The discharge was observed within 48 hours after the procedure, resulting in epithelialization of the microablative zone. During this period, the patient uses a special external wound healing agent. Usually starts from 3-4 days of exfoliation and swelling increases (Fig. 3 c). By day 7, this phenomenon gradually subsides, and erythema remains the only visible side effect (Fig. 3d). The duration of erythema depends on the parameters of laser exposure and the characteristics of skin vascularization. According to the author's observations, erythema lasts no more than 3 months.
Loss of patient social activity after FA procedure lasts from 5 to 10 days.
To prevent scarring and manifestations of post-inflammatory pigmentation, care must be taken with the skin. Decorative cosmetics can be used from 4-5 days. A prerequisite for good results is the use of at least 3 months after a sunscreen cosmetic procedure with a high level of protection (SPF at least 50). The risk of post-inflammatory pigmentation occurs in 20% of patients and is generally higher in skin patients. Phototype IV-V. Such hyperpigmentation is temporary and can last from 1 week to 3 months, which also depends on the depth of treatment and the area of the treated area. For its prevention 1-2 weeks before the procedure and during the next 2 weeks, external agents based on hydroquinone (4%) and tretinoin (0. 1%) are prescribed. The main effects on facial skin after the FA procedure are as follows: clear tightening and reduction of skin excess, evenness of wrinkled skin surface, as well as skin affected by acne scars, reduction of dysfunction, porosity.
This method is also tested by the author and his colleagues to get rid of stretch marks on the skin. As clinical studies have shown, this method shows high efficiency in the elimination of almost all types of stretch marks, both of which are acquired during puberty and after childbirth. It has been stated that the healing process on the skin of the body is different than on the skin of the face.
Skin reshaping mechanism when using fractional laser
Let's consider the mechanism of skin regeneration when using fractional lasers.
After being exposed to a laser, aseptic inflammation develops in the area of the micro-wound that forms. The more aggressive the laser exposure, the clearer the inflammatory response, which, in fact, stimulates the post-traumatic release of growth and infiltration of tissue damaged by fibroblasts. The reaction that comes automatically is accompanied by an explosion of cell activity, which inevitably leads to the fact that fibroblasts begin to produce more collagen and elastin. The skin remodeling process involves three phases of classical regeneration:
- phase I - changes (tissue inflammation). Starts immediately after damage;
- phase II - germination (tissue formation). Starting 3-5 days after injury and lasting about 8 weeks;
- phase III - tissue remodeling. Lasts from 8 weeks to 12 months.
It should be noted that all three phases of skin remodeling are observed both after fractional phototrolysis and after fractional ablation. But in the first case, the damaging laser effect is quite aggressive, as a result of which the inflammatory circulation changes are never too wild.
A completely different image is observed after exposure to fractional ablation lasers. The trauma caused by this laser breaks down the blood vessels, and the blood cells along with the serum are released into the surrounding tissue. The full mechanism of skin regeneration - phase change begins - aseptic inflammation develops. Platelets released from damaged vessels play an important role in activating blood clotting and releasing chemoxic factors that, in turn, platelets, leukocytes, and other fibroblasts are attracted to. Leukocytes, particularly neutrophils, participate in the cleansing of destroyed tissues, removing fragments of necrotic tissue, which is partially destroyed by phagocytitis, and partially excreting into the skin surface in the form of microscopic fragments consisting of epidermal and skin tissue substrates and melanin - microepidermal necrotic fragments (MENO).
The germination phase begins within 5 days. During this period, neutrophils are replaced by monocytes. Monocytes, keratinocytes and fibroblasts continue to influence growth factors and at the same time are under their inverted influence. Keratinocytes stimulate epidermal growth and release of growth factors needed to stimulate collagen production by fibroblasts. During this phase, new blood vessels form, and the extracellular matrix is intensively formed.
The final, reconstructive healing phase, after fractional laser exposure lasts several months.
By the 5th day after injury, the fibronectin matrix "fits" along the axis where the fibroblasts line up and where collagen will build. An important role in the formation of this matrix is played by altering the growth factor β (TGF-β is the chemotoxic quagant for fibroblasts), as well as other growth factors. The main form of collagen in the early phase of wound healing is type III collagen (this type of collagen is located in the upper layer of the dermis, just below the basal layer of the epidermis). The longer the phase of change, the more type III collagen will be produced, but in any case, the amount increases a maximum of 5 to 7 days after injury. Type III collagen is gradually being replaced by Type I collagen for about a year, which strengthens the strength of the skin. Blood circulation is gradually normalized, the skin becomes smoother and acquires a natural color.
Comparative analysis of skin reshaping laser method
Summarizing the above, the following is a diagram showing the relationship between the effectiveness and safety of laser skin reshaping techniques.
Advantages of fractional track rejuvenation methods. The advantages of fractional methods used in clinical practice include:
- controlled minimum skin damage. Histological studies performed after the procedure showed an increase in the number of papillae in the dermis, which characterized changes in the skin as productive regrowth;
- effective rejuvenation: skin becomes thicker, significantly (more than 400% (! )) increases collagen and elastin production;
- short healing time: average 3 days after FF and 7-14 days after PA;
- minimum risk of hyperpigmentation;
- possible procedure in patients with thin skin;
- ability to have a healing effect on any part of the body;
- possibility of using mild types of anesthesia: with fractures of phototrolysis, only local application anesthesia is used; for fractional ablation, a combination of conduction and infiltration anesthesia is required;
- loss of telangiectasias (due to rupture of blood vessels in many places so recovery is not possible).
Key indications for fractional treatment
Instructions for fractional photolysis:
- increased skin density in the early stages of aging. The FF procedure is quite simple and can be performed without fear. The therapeutic effect can be given on the neck, décolleté, arms, abdomen, thighs, mammary glands;
- skin shooting;
- hyperpigmentation, melasma;
- hypertrophic scars;
- stretch mark.
Instructions for Fractional Ablation:
- wrinkles of varying severity - from fine lines to very noticeable (in the form of wrinkles);
- loss of age-related skin elasticity and firmness;
- excess skin on the eyelids, neck, face (as an alternative to plastic surgery);
- uneven skin texture;
- significant skin photo;
- acne scars;
- cicatricial defects in skin after injury, surgery;
- hyperpigmentation: melasma, lentiginosis, speckled pigmentation, etc.
- vascular dysfunction;
- skin stretch marks;
- active keratosis.
In conclusion, a few words about the prospects of the use of laser technology in aesthetic medicine. We should respect manufacturers that they are beginning to pay more attention to the safety of medical procedures using lasers. Technology is constantly evolving. However, the safety of this method is often sacrificed to increase its effectiveness. Or otherwise. Compromise is found in the new principle of laser radiation delivery to tissues. It should be noted that the types of salts remain the same: erbium, carbon dioxide, neodymium. This indicates that:
- first, laser skin remodeling is recognized as the most effective today; Second, the extent of aesthetic and dermatological problems solved by this method is enormous - from skin rejuvenation to congenital and acquired pathological skin treatment;
- third, with the advent of fractional technology, the safety and effectiveness of treatment have been predictable.













































































